Welcome to the latest edition of AI Quick Bytes, where we turn the complexities of AI into actionable insights for today's tech and business leaders. This week, we're diving deep into the transformative power of AI, with expert strategies for mastering Open Data Architecture, cutting-edge trends from Microsoft, and a head-to-head showdown between Vector Databases and traditional RDBMS. Plus, we've got the perfect ChatGPT prompts to help you make business decisions like a pro. Ready to unlock the full potential of AI in your enterprise?
Quick bits
Strategy: Mastering Open Data Architecture: Create a robust foundation for AI success with a comprehensive open data architecture blueprint.
Trends: AI Transformation at Microsoft: Satya Nadella reveals the ambitious AI initiatives transforming Microsoft and the industry.
Tools: Vector Databases vs. RDBMS: Explore the rise of vector databases and what it means for traditional RDBMS.
Prompts: Copy these ChatGPT prompts to make business decisions like Warren Buffett, or at least to get insightful feedback based on classic strategies.
Let’s Get To It!

Deeper Bytes
Strategy
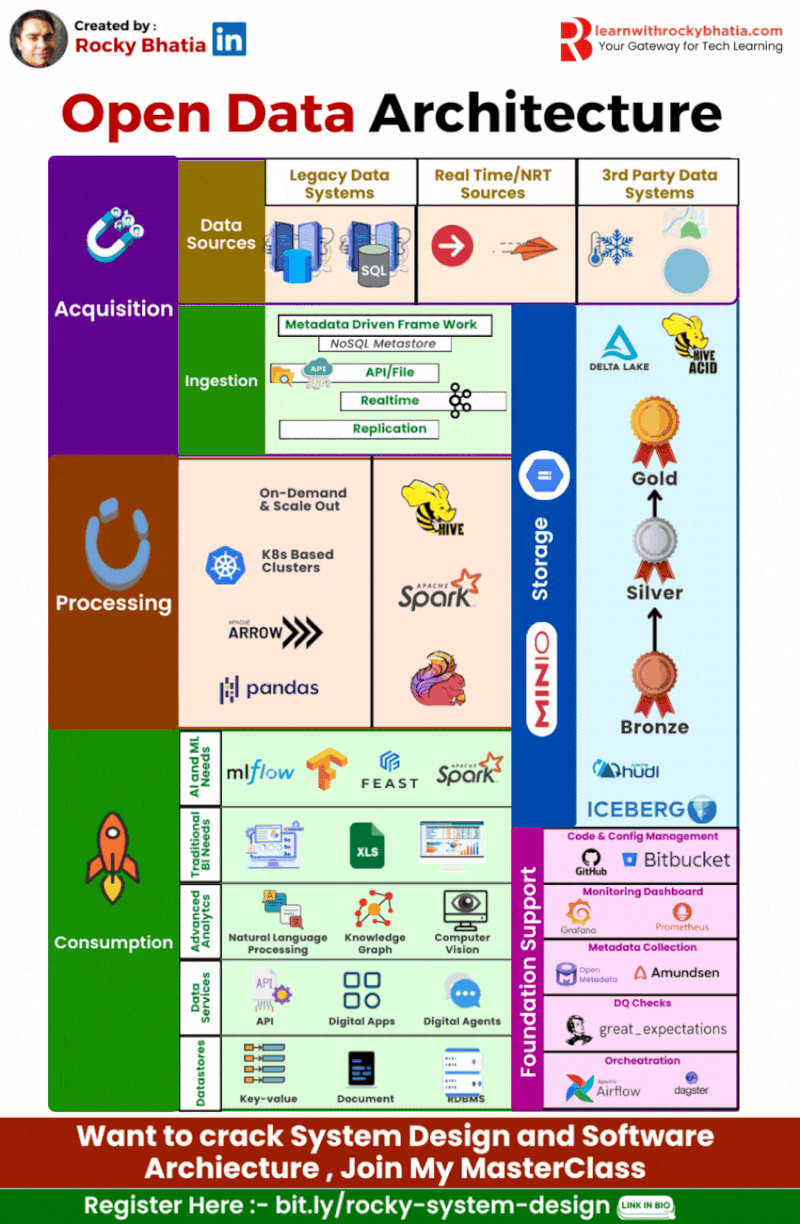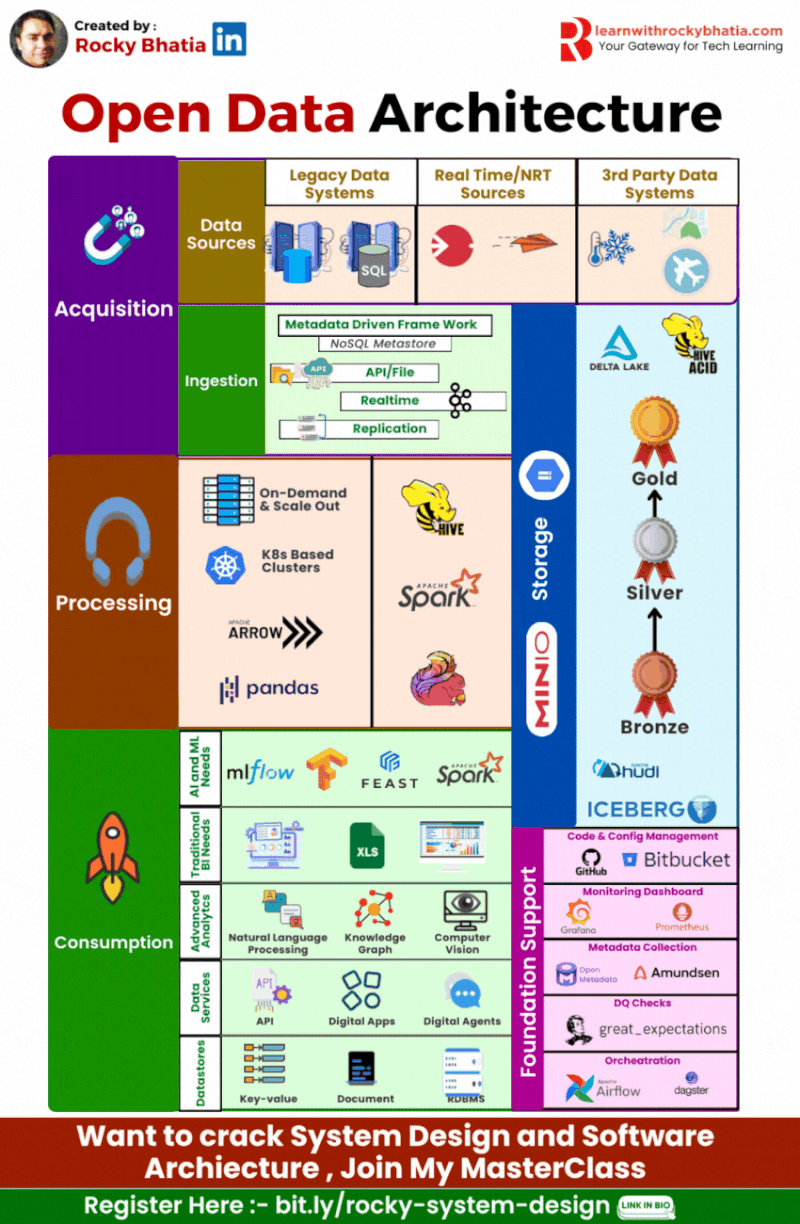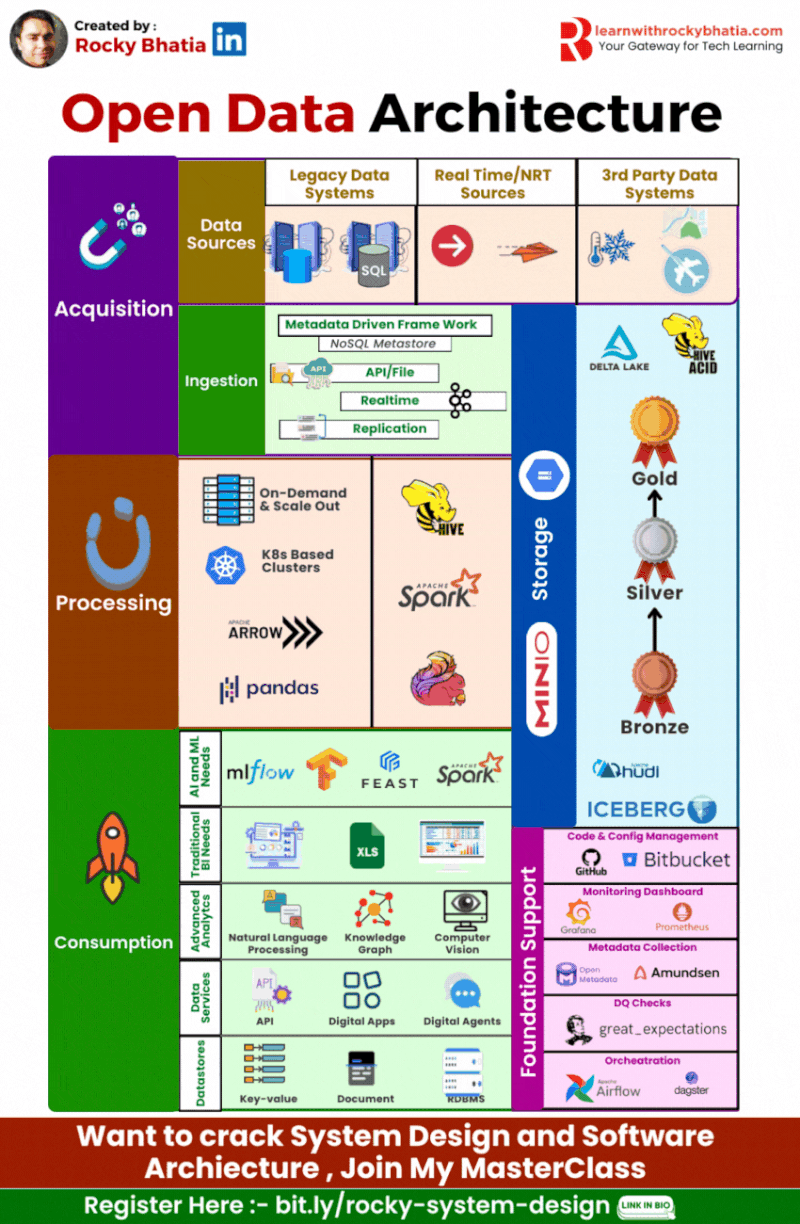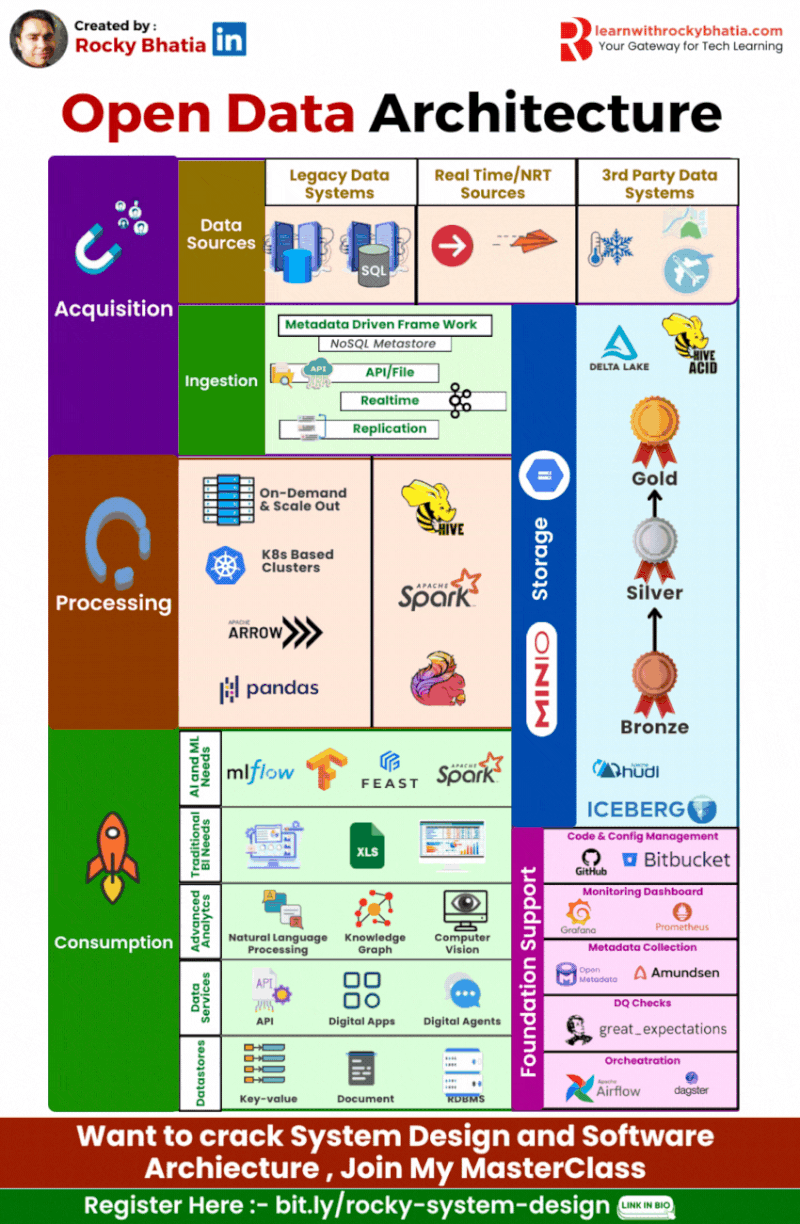
Strategy Insight: Mastering Open Data Architecture with Rocky Bhatia
One common pitfall in enterprises is rushing into AI without a solid data foundation. Think of it like mining for gold: without a strategic approach, you might find a nugget here and there, but systematic success requires a well-thought-out plan. Enter Open Data Architecture, the bedrock of reliable and scalable AI.
Key Components of Open Data Architecture:
🔹 Data Source: Collect data from diverse origins like sensors, databases, and applications.
🔹 Ingestion: Efficiently bring in data through batch or stream processing for timely insights.
🔹 Processing: Transform, clean, and enrich data for usability.
🔹 Data Lake: Centralize raw data for flexible analysis.
🔹 Delta Lake: Enhance your Data Lake with ACID transactions for data reliability and consistency.
🔹 Consumption: Deliver processed data to various applications and end-users.
🔹 Data Service: Provide structured access to data via APIs and services.
🔹 Analytics Service: Empower decision-making with advanced analytics and visualisation tools.
🔹 Data Quality: Ensure high-quality data with robust validation and cleansing processes.
🔹 Data Governance: Implement policies and practices to manage data integrity, privacy, and compliance.
Why Open Data Architecture?
Adopting an Open Data Architecture integrates quality and governance, turning raw data into actionable insights. This holistic strategy drives innovation and competitive advantage, ensuring your AI initiatives are not just successful, but repeatedly so.

Trends
The Age of AI Transformation: Microsoft’s Bold Moves
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, recently highlighted the company's significant strides in AI, underscoring their commitment to revolutionizing the field.
Empowering Educators and Students: Microsoft's AI initiatives aim to enhance educational outcomes, demonstrating the potential of small models tailored for specific use cases.
Refinement of AI Models: Microsoft’s focus on refining small models for targeted applications showcases their dedication to practical, impactful AI solutions.
This positive AI narrative stands out amidst the fear-mongering, emphasizing how AI can drive meaningful change in education and beyond. It’s a testament to the transformative power of AI when strategically implemented and ethically guided.

Tools
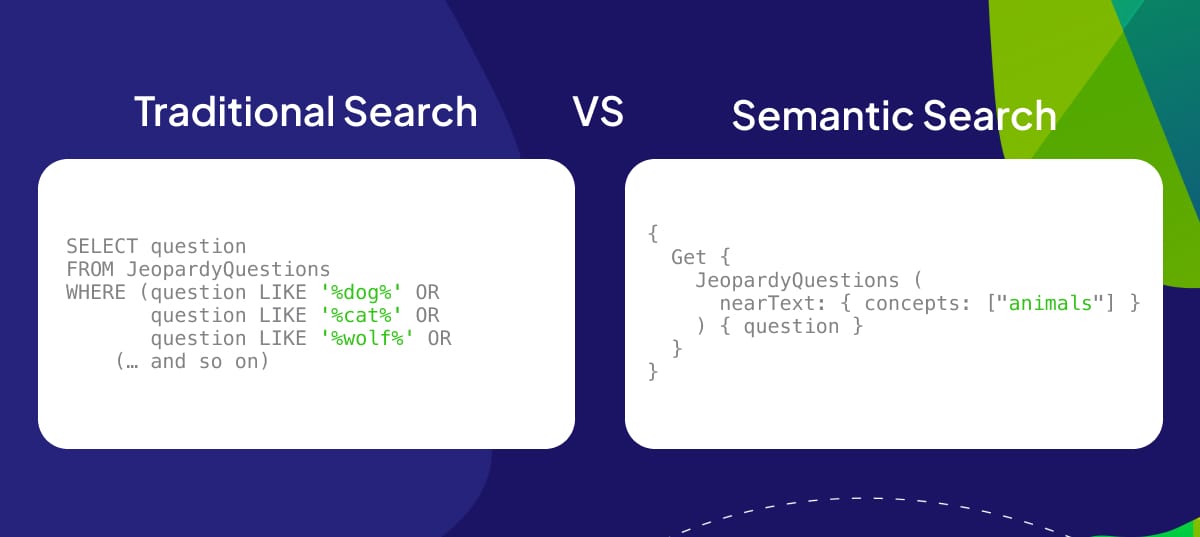
Tool Spotlight: Vector Databases vs. RDBMS
Database Search
In the world of data management, Vector Databases and Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) serve distinct purposes. Let’s delve into their key differences:
Vector Databases
Overview:
Designed for vectorized data, commonly used in AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics. These databases excel at similarity searches and high-dimensional data processing.
Strengths:
High-dimensional data handling: Efficiently processes complex, multi-dimensional vectors.
Similarity search: Optimized for nearest-neighbor searches and similarity queries.
AI/ML integration: Seamlessly integrates with machine learning pipelines and tools.
Weaknesses:
Specialized use: Not suitable for traditional transactional data or complex relational queries.
Newer technology: Less mature than RDBMS, with fewer available tools and community support.
Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS)
Overview:
Traditional databases that manage structured data using tables, rows, and columns. They excel at handling transactional data and ensuring data integrity through ACID properties.
Strengths:
Mature technology: Well-established with a vast ecosystem of tools, support, and expertise.
Data integrity: Strong ACID compliance ensures reliable transaction processing.
Versatile querying: Powerful SQL capabilities for complex relational queries.
Weaknesses:
Scalability issues: Can struggle with large-scale, high-velocity data without significant tuning.
Complexity with unstructured data: Less efficient at handling unstructured or semi-structured data.
Performance: Not optimized for high-dimensional vector searches.
Comparison Table: Vector Databases vs. RDBMS
Feature | Vector Databases | Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) |
|---|---|---|
Data Type | High-dimensional vectors | Structured data (tables, rows, columns) |
Primary Use Case | AI/ML applications, similarity searches | Transactional data, relational queries |
Query Language | Specialized APIs, often no standard query language | SQL |
Performance | Optimized for vector searches | Optimized for relational queries |
Scalability | High scalability for vectorized data | Can struggle with large-scale data |
Data Integrity | Basic consistency, lacks full ACID properties | Strong ACID compliance |
Maturity | Emerging technology, growing ecosystem | Mature technology, extensive ecosystem |
Integration with AI/ML | Seamless integration | Limited integration |
Tooling and Support | Limited, still developing | Extensive, well-established |
Complex Queries | Limited capabilities for complex joins/queries | Advanced capabilities for complex joins/queries |
Conclusion
While Vector Databases and RDBMS serve different purposes, understanding their strengths and weaknesses helps in choosing the right tool for the job. Vector Databases are indispensable for AI and machine learning applications, offering unparalleled performance for similarity searches and handling high-dimensional data. On the other hand, RDBMS remains the go-to solution for transactional data processing, offering robust data integrity, mature tooling, and versatile querying capabilities. By leveraging the strengths of each, businesses can effectively manage and utilize their data to drive innovation and efficiency.

Training
Step into the Future with Hyperdrive! Are you a Product Manager looking to master AI or earn your AI Certified Scrum Product Owner license? Hyperdrive offers top-tier Agile training, consulting, and staffing—power up your career in AI today!

Schedule :

Prompts

Classic Strategies
A nice set of prompts by TJ Larkin Jr. for different business strategies and matrixes. In the comment section of this post there is feedback that advises to leverage these prompts with caution as these generic prompts will provide at best generic responses. MoreThanDigital promises Data Driven Strategic Management for everyone. They are in waitlist status at the moment. Would love to know if anyone has been able to kick the tires.
The direction we are racing toward is the ability to provide specialized reporting based on bespoke company data with groomed smaller targeted niche models that cost less to maintain and provide better/faster responses. For now I still like leveraging the below types of prompts that you can provide context and tweak as it empowers you to build a strawman very quickly that you can then iterate on and would be proud to present to your peers and leadership team.
Prompts:
1. 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝘀𝗽𝗲𝗰𝘁 𝗧𝗵𝗲𝗼𝗿𝘆
Prompt: "Utilize Prospect Theory to assess [my business decision]. Understand how people perceive gains and losses and how that can influence decision-making."
2. 𝗥𝗶𝘀𝗸-𝗥𝗲𝘄𝗮𝗿𝗱 𝗔𝗻𝗮𝗹𝘆𝘀𝗶𝘀
"Analyze [my business decision] through Risk-Reward Analysis. Evaluate the potential risks against the potential rewards to understand the balance and make an informed decision."
3. 𝗖𝗿𝗼𝘀𝘀-𝗙𝘂𝗻𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗣𝗲𝗿𝘀𝗽𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲
"Evaluate [my business decision] with a Cross-Functional Perspective. Involve multiple departments or teams to ensure a comprehensive understanding of how the decision affects various aspects of the business."
4. 𝗧𝗵𝗲 𝗢𝗢𝗗𝗔 𝗟𝗼𝗼𝗽 (𝗢𝗯𝘀𝗲𝗿𝘃𝗲, 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗲𝗻𝘁, 𝗗𝗲𝗰𝗶𝗱𝗲, 𝗔𝗰𝘁)
"Use the OODA Loop to evaluate [my business decision]. Cycle through observing the situation, orienting yourself, making a decision, and taking action, then repeating as necessary."
5. 𝗣𝗿𝗲-𝗠𝗼𝗿𝘁𝗲𝗺 𝗔𝗻𝗮𝗹𝘆𝘀𝗶𝘀
"Utilize Pre-Mortem Analysis to assess [my business decision]. Imagine a future failure of the decision and work backward to identify potential causes and mitigation strategies."
6. 𝗕𝗹𝘂𝗲 𝗢𝗰𝗲𝗮𝗻 𝗦𝘁𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗴𝘆
"Apply the Blue Ocean Strategy to evaluate [my business decision]. Focus on creating uncontested market space rather than competing in existing industries."
7. 𝗦𝗰𝗲𝗻𝗮𝗿𝗶𝗼 𝗣𝗹𝗮𝗻𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴
"Apply Scenario Planning to assess [my business decision]. Create different future scenarios and analyze how the decision performs in each to identify potential risks and opportunities."
8. 𝗧𝗵𝗲 𝗘𝗶𝘀𝗲𝗻𝗵𝗼𝘄𝗲𝗿 𝗠𝗮𝘁𝗿𝗶𝘅
"Use the Eisenhower Matrix to evaluate [my business decision]. Categorize tasks or elements based on urgency and importance to prioritize effectively."
9. 𝗧𝗲𝗺𝗽𝗼𝗿𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗶𝘀𝗰𝗼𝘂𝗻𝘁𝗶𝗻𝗴
"Use Temporal Discounting to analyze [my business decision]. Consider how the value of outcomes changes over time and how that might influence the decision-making process."
10. 𝗥𝗲𝘀𝗼𝘂𝗿𝗰𝗲-𝗕𝗮𝘀𝗲𝗱 𝗩𝗶𝗲𝘄
"Apply the Resource-Based View to evaluate [my business decision]. Focus on leveraging the company's internal strengths and weaknesses in relation to external opportunities and threats."
We value your voice! Send us your thoughts, topic suggestions, questions, or comments. Together, we’ll navigate the exciting world of AI, one engaging interaction at a time.
Until next time, let’s decode the future of AI, one byte at a time!